fungi life cycle explained
Home explained full fungi life recruiting wallpaper. As part of their life cycle fungi produce spores.

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Some fungi are multicellular while others such as yeasts are unicellular.

. Life Cycle Of Receptors G Proteins And Second Messengers Definition Examples Camp Ip3 Pip2 Functions And More Life Cycles Plasma Membrane Cell Biology. Fungal life cycles are unique and complex. Fungi exist primarily as filamentous dikaryotic organisms.
This is how the fungus reproduces asexually. In most fungi the asexual reproductive cycle comes first with a sexual reproductive cycle to follow. Meiosis reduction division restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates the.
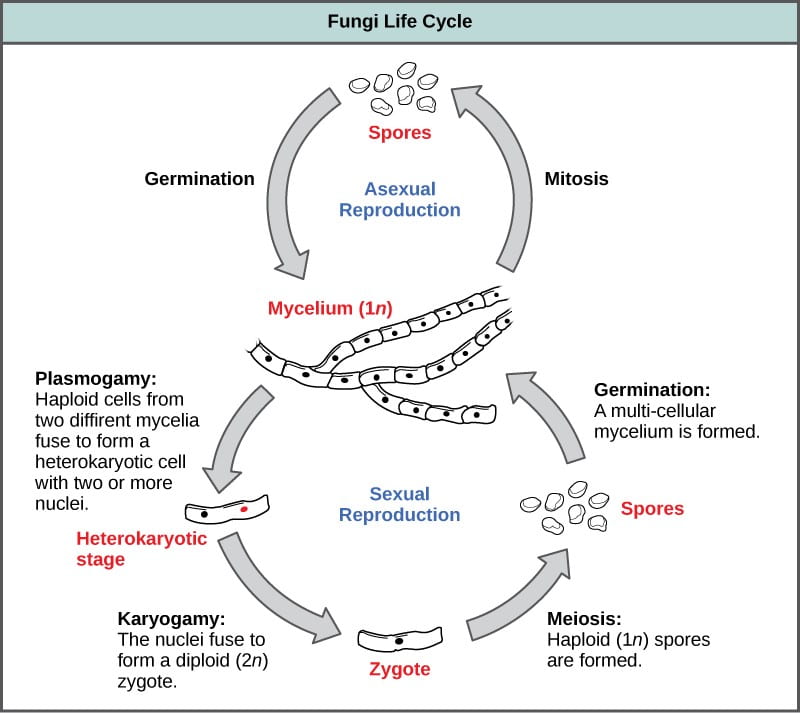
All fungi begin their life cycle in this stage. This dikaryotic cell produces ascogenous hyphae and subsequently asci. Spore Haploid The spore phase is the initial stage of the fungal life cycle.
Life cycle of The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. When hyphae from 2 genetically different haploid mycelia meet release pheromones. Macroscopic fungi such as morels mushrooms puffballs and the cultivated agarics available in grocery stores represent only a small fraction of the diversity in the kingdom Fungi.
Mushroom spores are tiny microscopic reproductive units that are produced by fungi as well as some. Fragments of hyphae can grow new colonies whereas during budding a bulge forms on the side of the cell the nucleus divides mitotically and the bud ultimately detaches itself from the mother cell. Fungi reproduce sexually either through cross- or self-fertilization.
After the fungi has become. When the mycelium grows and develops it might encounter another fungi. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts moulds and mushrooms.
For most of the molds indoors fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. Despite the name this doesnt have anything to do with bacteria or disease. Sexual reproduction is carried out by diffusion of compatable nuclei from two parent at a definite state in the life cycle of fungi.
Produced by fruiting bodies such as the edible portion of a mushroom these spores germinate and grow into new adult fungi under suitable conditions in terms of temperature moisture and availability of organic matter ie food. The life cycle of a mushroom begins and ends through five stages of evolutionary phases beginning as a fungal spore seeds and completing its cycle as a mature fruiting body the part of a mushroom we all identify and know that releases new spores to create a new cycle all over again. Hyphae are root-like threads composed of haploid cells.
Under favourable conditions each conidium germinates by germ tube which ultimately grows into somatic mycelium of the new individual. Fungi may reproduce either sexually or asexually. Spores produced by mature fungi are released into the surrounding environment where they divide and grow into hyphae.
Mushroom spores can detect. Two different mating types represented as type and type are involved. Fungi reproduce sexually either through cross- or self-fertilization.
The molds for example are a large group of microscopic fungi that include many of the economically important plant parasites allergenic species and opportunistic pathogens of humans and other animals. Mycelium Diploid At the point when the mycelium develops and creates it may encounter other fungi. Fungi begin their life as a spore released by adult cells and they go on to release spores later as well.
When two hydra of opposite strain - come into contact the two cell types fuse to create one cell with two nuclei. Sex- signaling molecules just their cytoplasm fuses. Fungi life cycle explained Sunday February 27 2022 Edit.
This fusion from cytoplasm from 2. Haploid fungi form hyphae that have gametes at the tips. The process of sexual reproduction involves three phases.
Of these eight nuclei six degenerate and only two nuclei survive. This fused cell grows into the fruiting body also known as the mushroom. The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells.
Fungal life cycles are unique and complex. Two different mating types represented as type and type are involved. This cycle all takes place.
With asexual reproduction a lone individual produces exact clones of itself. These two smaller cycles make up the life cycle of fungi. Fungi can reproduce asexually by fragmentation budding or producing spores.
Have aquatic spores that infect amphibians. During sexual reproduction the changes involved in the process occur in regular sequence in cyclic order. The two nuclei fuse into a diploid nuclei and meiosis further divides the nuclei into four.
Haploid fungi form hyphae that have gametes at the tips. Most fungi are microscopic but many produce the visible fruitbodies we call mushrooms. All fungi start as haploid spores.
If the two fungi are. This is the first stage in the life cycle of a fungus. Life cycle of fungi.
This form of the fungus life cycle is only advantageous in locations where the clones will thrive. Life Cycle of Fungi. Spore germ hypha mature mycelium.
In this electron micrograph of a mushroom gill the four spores produced by meiosis seen in the center of this picture are carried on a clublike sporangium visible to the left and right. The Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Spores Hyphae Mycelium Hyphal knot Mushroom. Brundrett 1990 showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould.
The Life Cycle of Fungi 1. Fungi can reproduce asexually by budding and many also have sexual reproduction and form fruitbodies that produce spores. The young ascus has a dikaryon ie two nucelei which fuse to form a diploid nucleus.
Sexual reproduction in fungi. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. This diploid nucleus divides by meiosis and then by mitosis To form eight nuclei.

Reproduction In Fungi Life Cycle Of Fungi Youtube

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Basidiomycota Life Cycle Study Com

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids

Fungi Life Cycle In Basidiomycetes Youtube
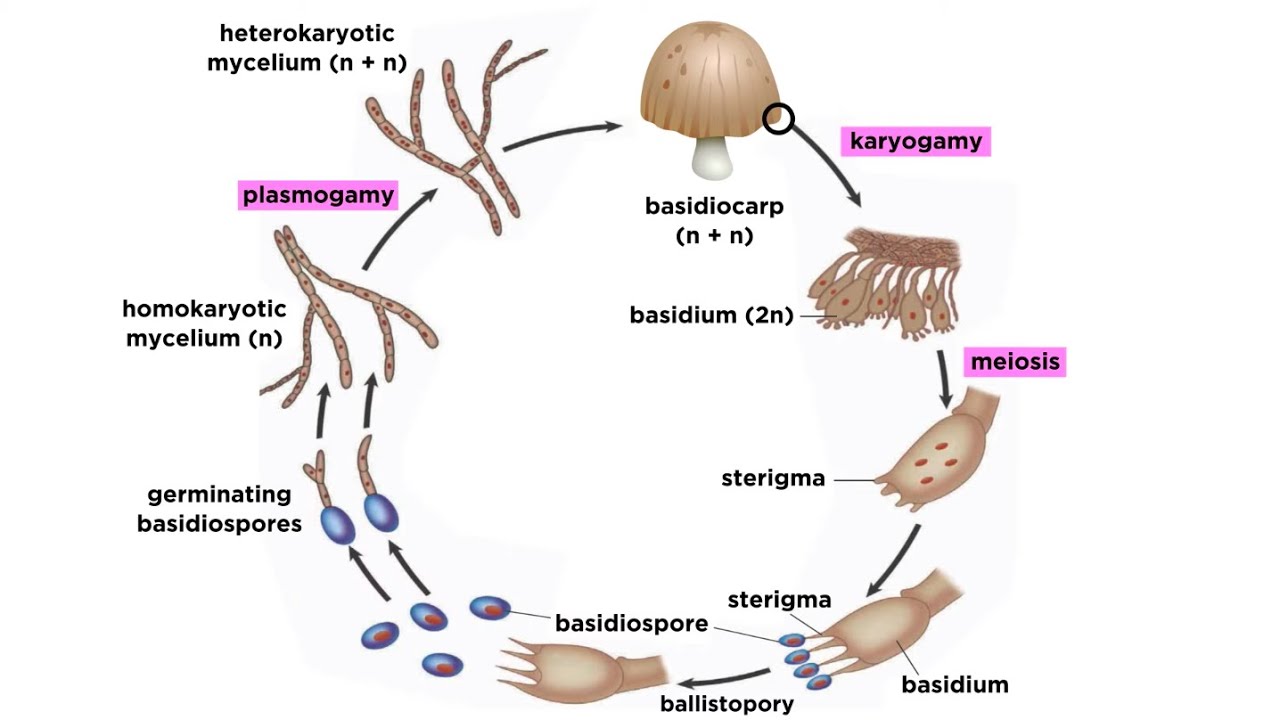
Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube

Life Cycle Of Aspergillus And Suggested Localization Of Ribotoxins Download Scientific Diagram

The Life Cycle Of Dictyostelium Discoideum Most Of Its Life This Download Scientific Diagram

Intro To The Fungi Life Cycle Plantsnap

The Moss Life Cycle Moss Gametophyte Reproduction Parts Diagram Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Life Cycle Of Receptors G Proteins And Second Messengers Definition Examples Camp Ip3 Pip2 Functions And More Life Cycles Plasma Membrane Adenylyl Cyclase
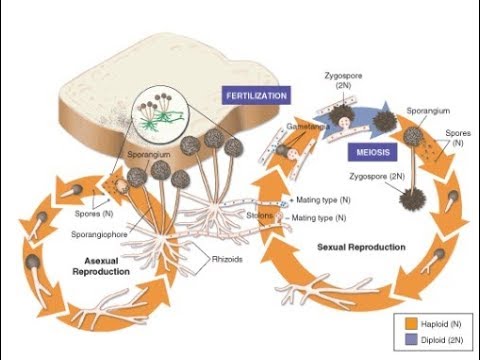
Life Cycle Of Fungus Black Bread Mold Rhizopus Stolonifer Youtube